# Quickstart - Github Sync
The purpose of this guide is to help you start building projects on Pipedream using GitHub Sync.
This guide assumes you:
- Have a Pipedream account
- Have a GitHub account
- Understand the basics of workflow development on Pipedream
- Are familiar with git-concepts (branches, commits, merges, etc)
- Are on an eligible plan (opens new window)
TIP
If you are new to Pipedream, we recommend starting with the basics of workflow development.
TIP
Users on the Free and Basic plan may preview GitHub Sync by enabling the feature when creating a new project. You will not be able to merge to production without upgrading. When you upgrade, you may enable or disable GitHub sync for projects at any time.
# Create a new project
Follow the steps below to create a new project and configure GitHub Sync.
TIP
This example uses Pipedream's OAuth integration with GitHub which will automaticallly create a a new, empty repo in GitHub. The OAuth integration requires the granting of extensive scopes so Pipedream can create and manage the integration. If you prefer not to use OAuth and configure the integration manually, follow the steps in Pipedream's docs to configure the integration using deploy keys. Deploy keys allow you to restrict Pipedream's access to a specific repo.
Go to https://pipedream.com/projects and click on Create Project.
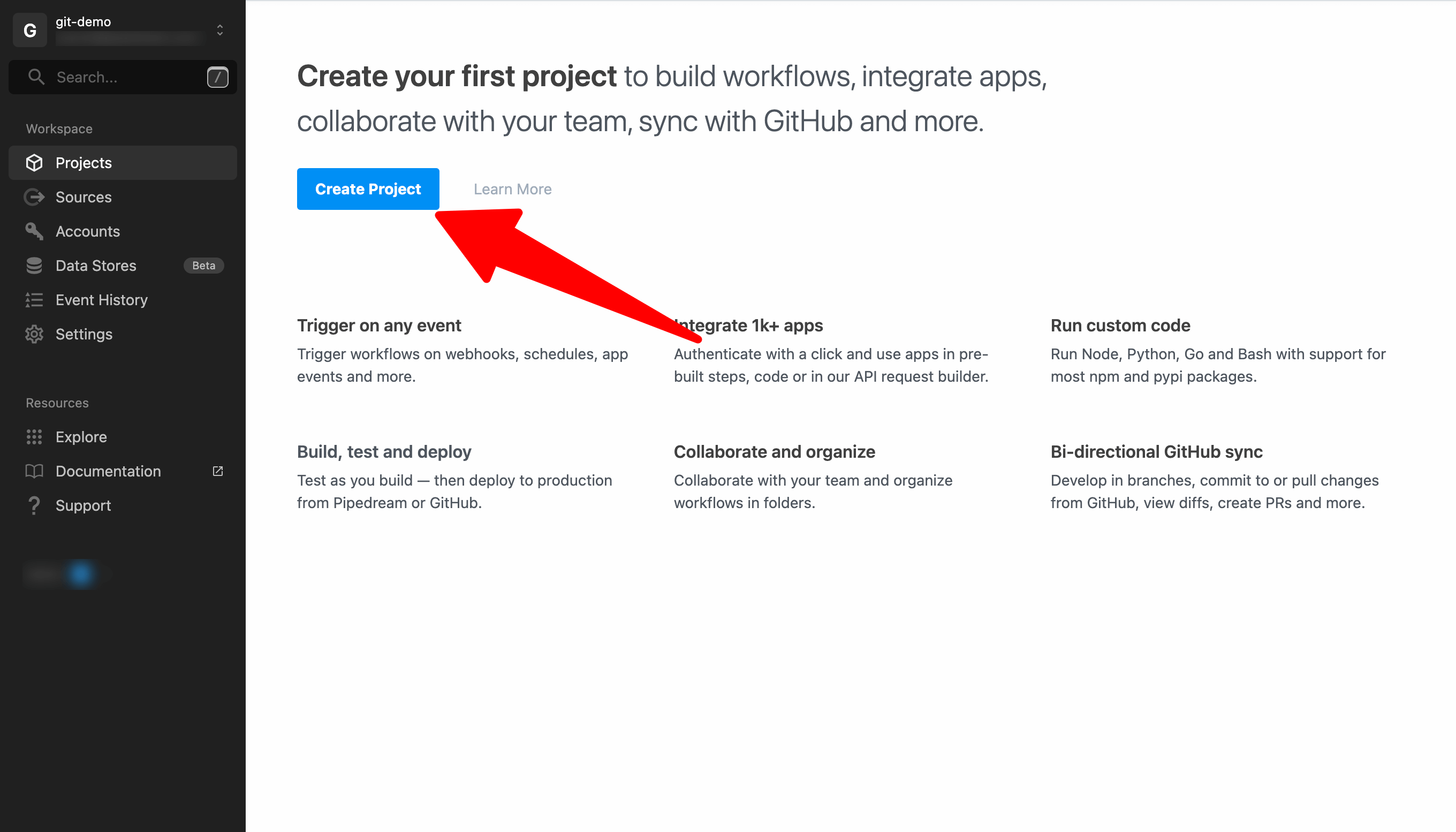
Enter a project name or click the icon to generate a random name and check the box to Configure GitHub Sync.
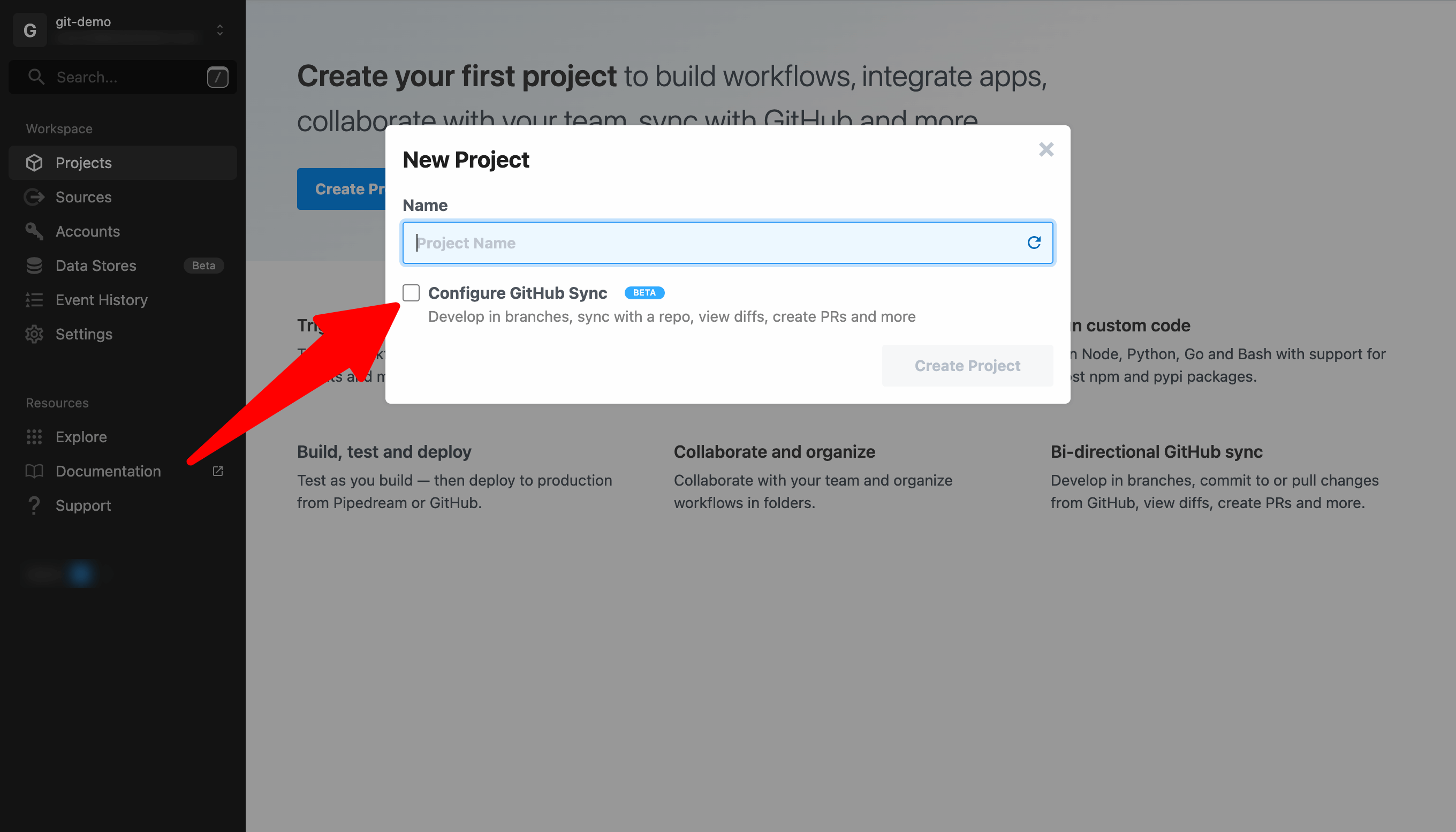
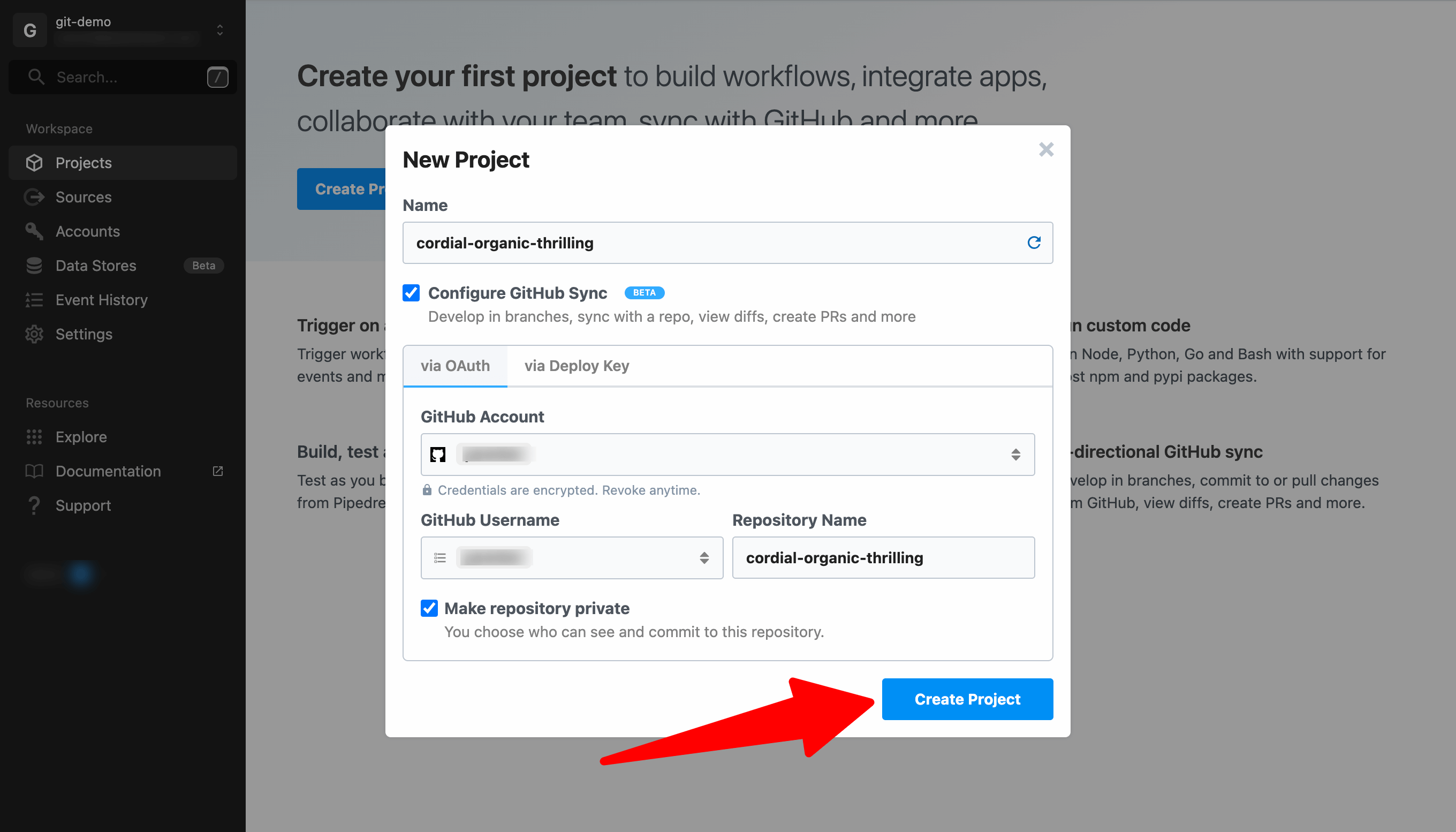
Select or connect a GitHub account, username and repo name and click Create Project.
# Create a branch to make edits
Once your project is ready, click on the Edit button.
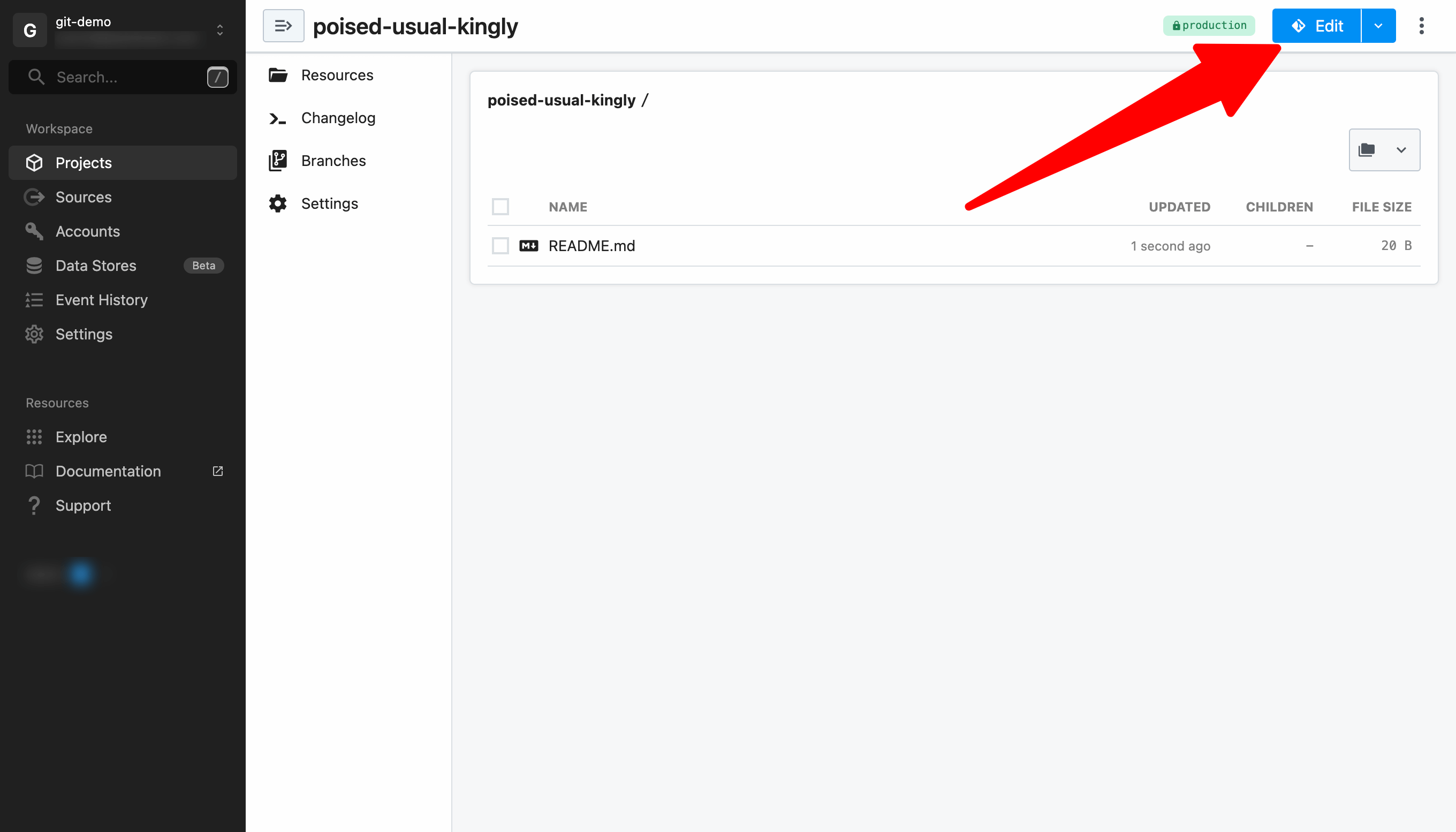
Since this is a new project, you will prompted to create a branch. You may accept the default branch name or customize it.
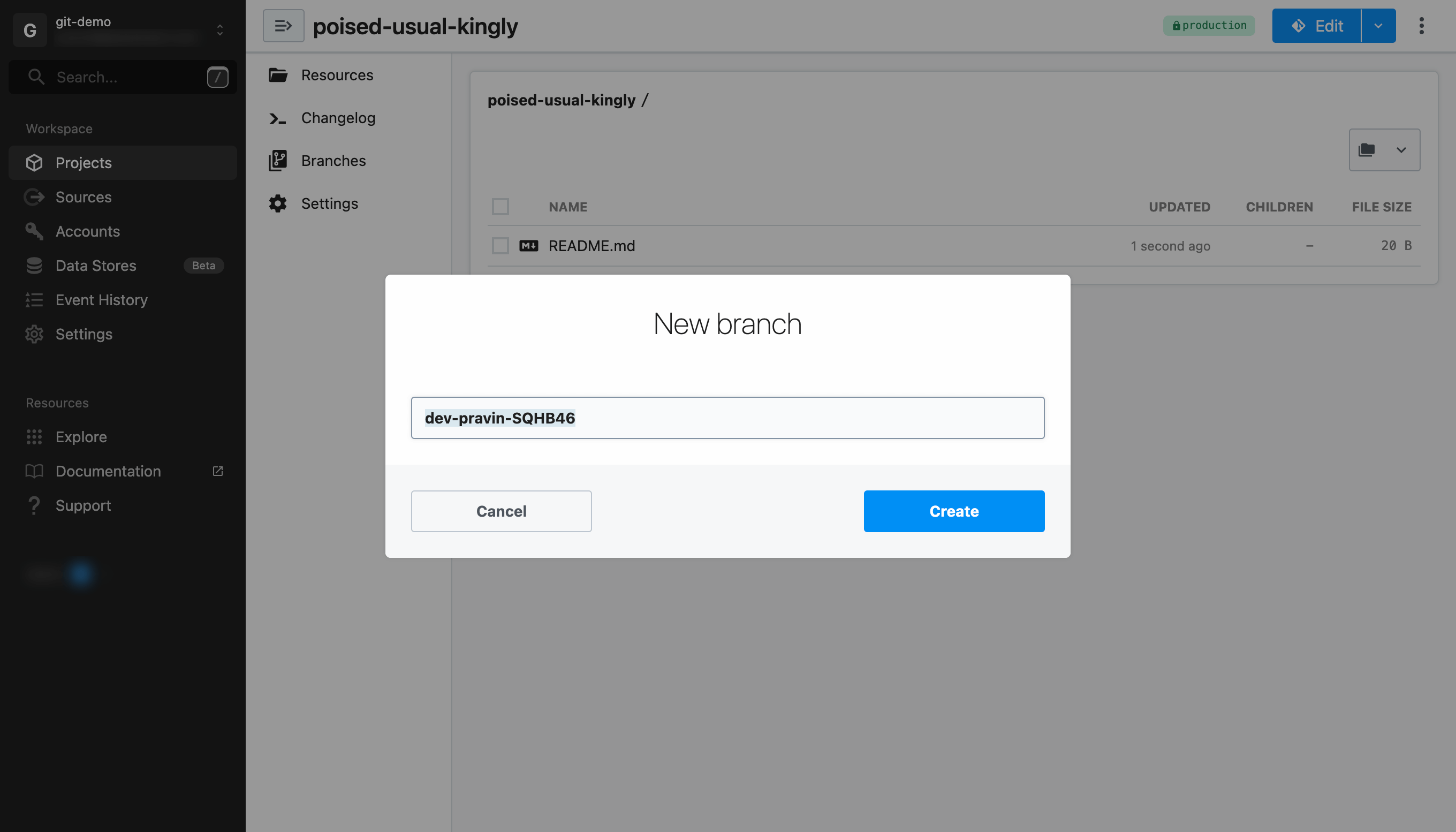
In the future, when you click Edit, Pipedream will load development mode for the last branch you were editing for the project. You may also create or select a different branch from the drop down menu.
TIP
When GitHub Sync is enabled, project resources may only be edited in a branch.
# Create a workflow in the editable branch
Once the branch is created, click the New button to create a workflow.
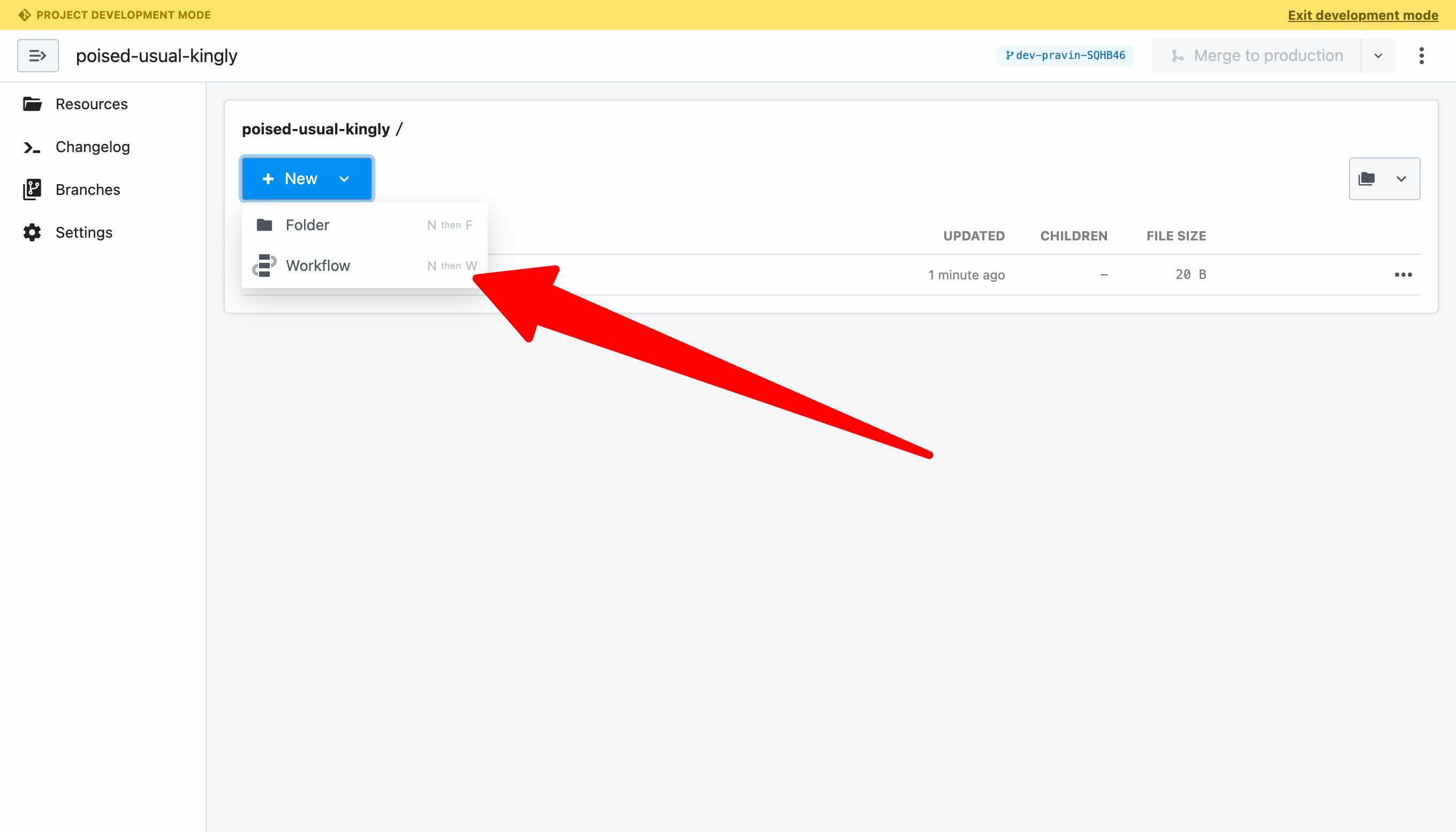
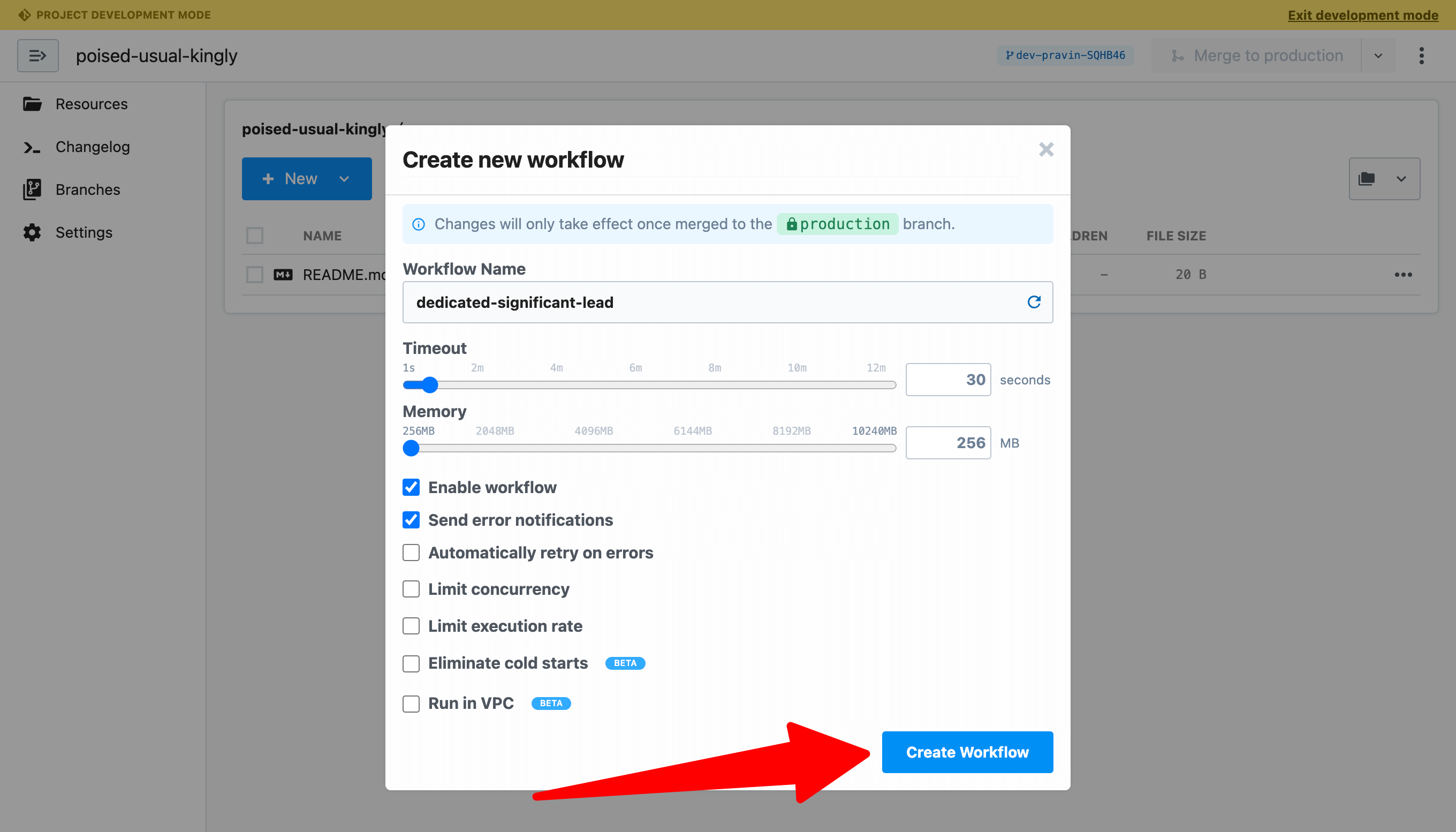
For this example, name the workflow and click Create Workflow to use the default settings.
Build a simple workflow with an HTTP trigger and Node code step.
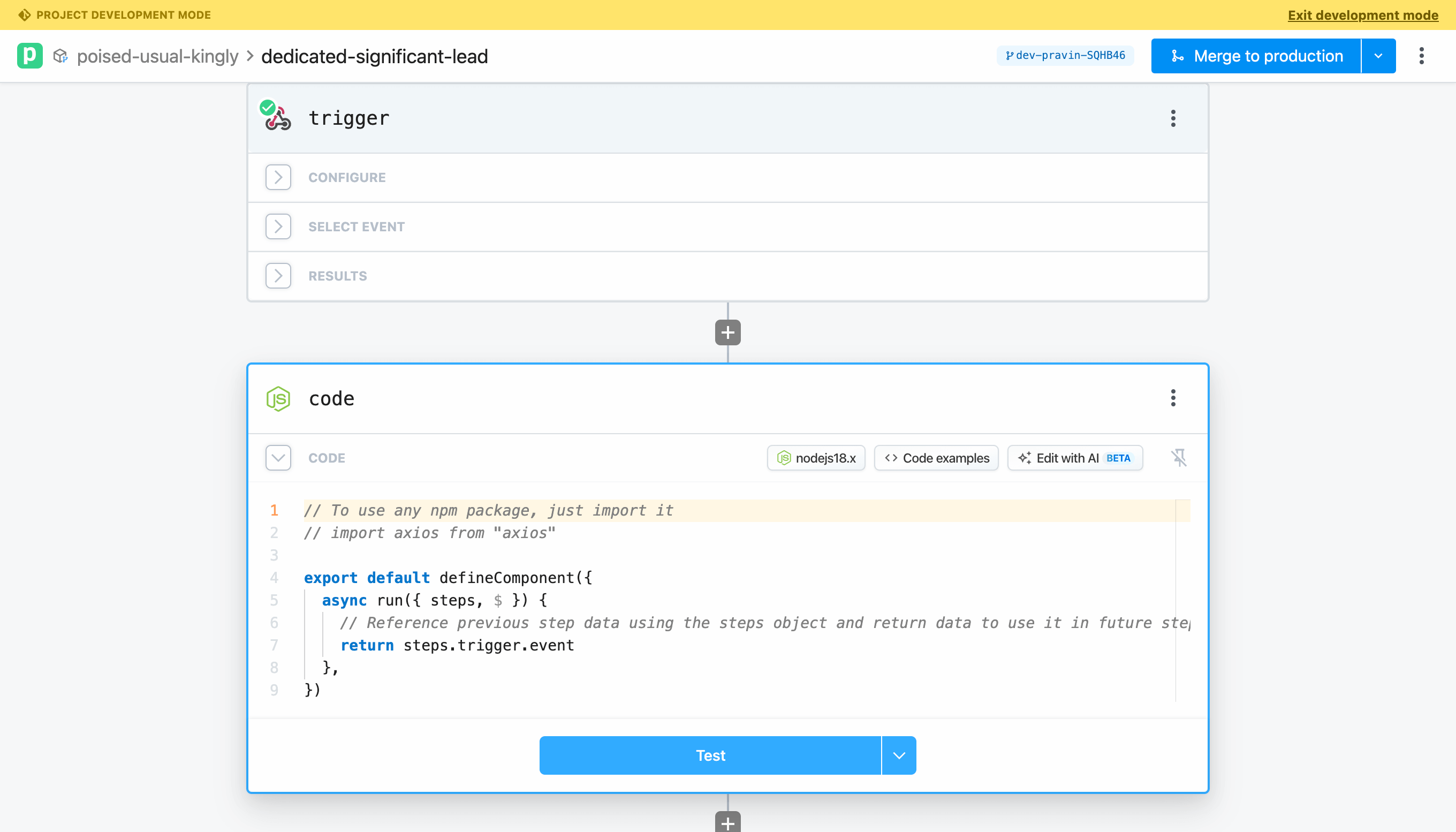
At this point, your workflow is saved, but changes have not been commited to GitHub. To do that, click on the dropdown menu and select Commit.
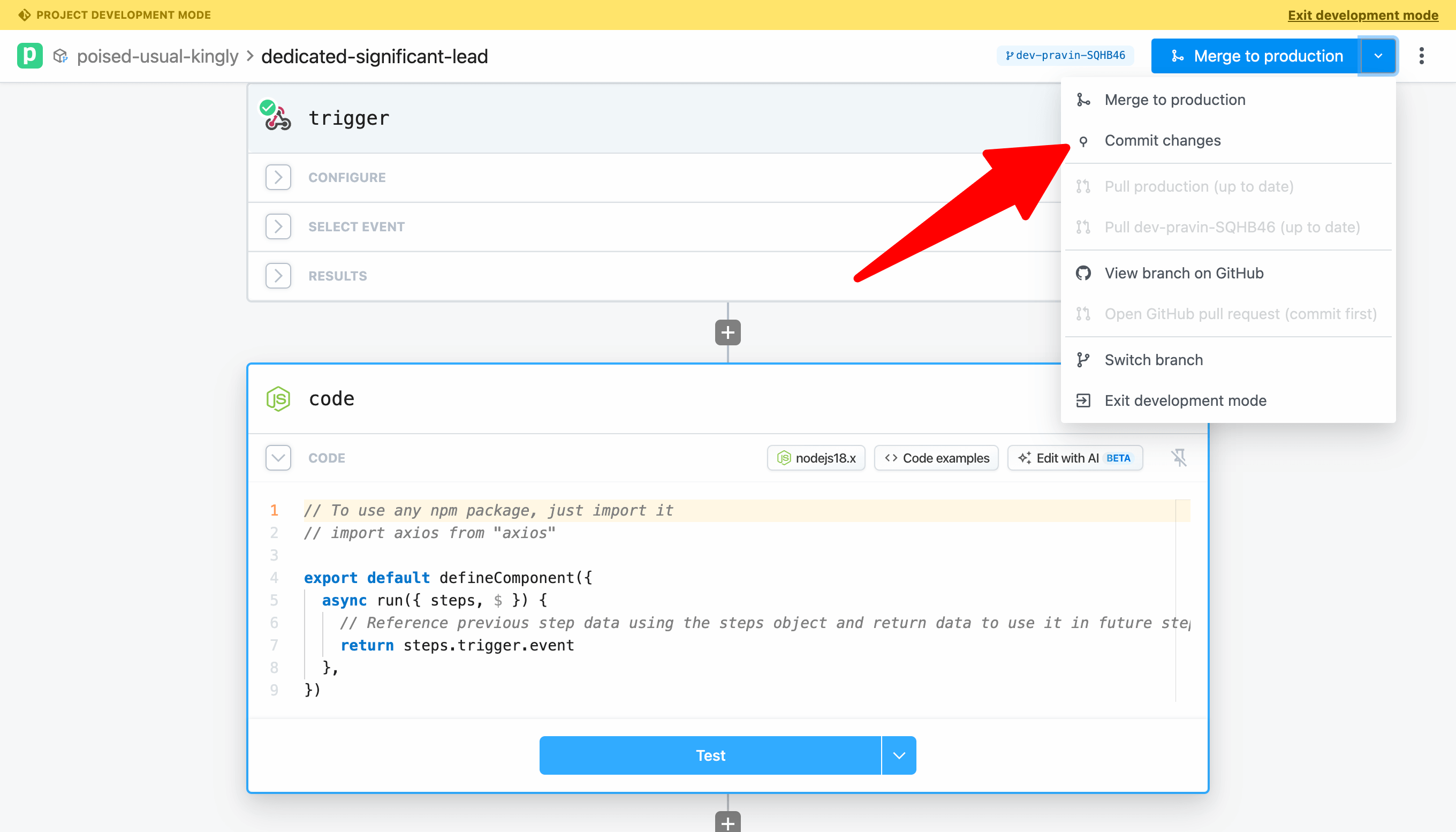
You may add an option commit message and complete the commit.
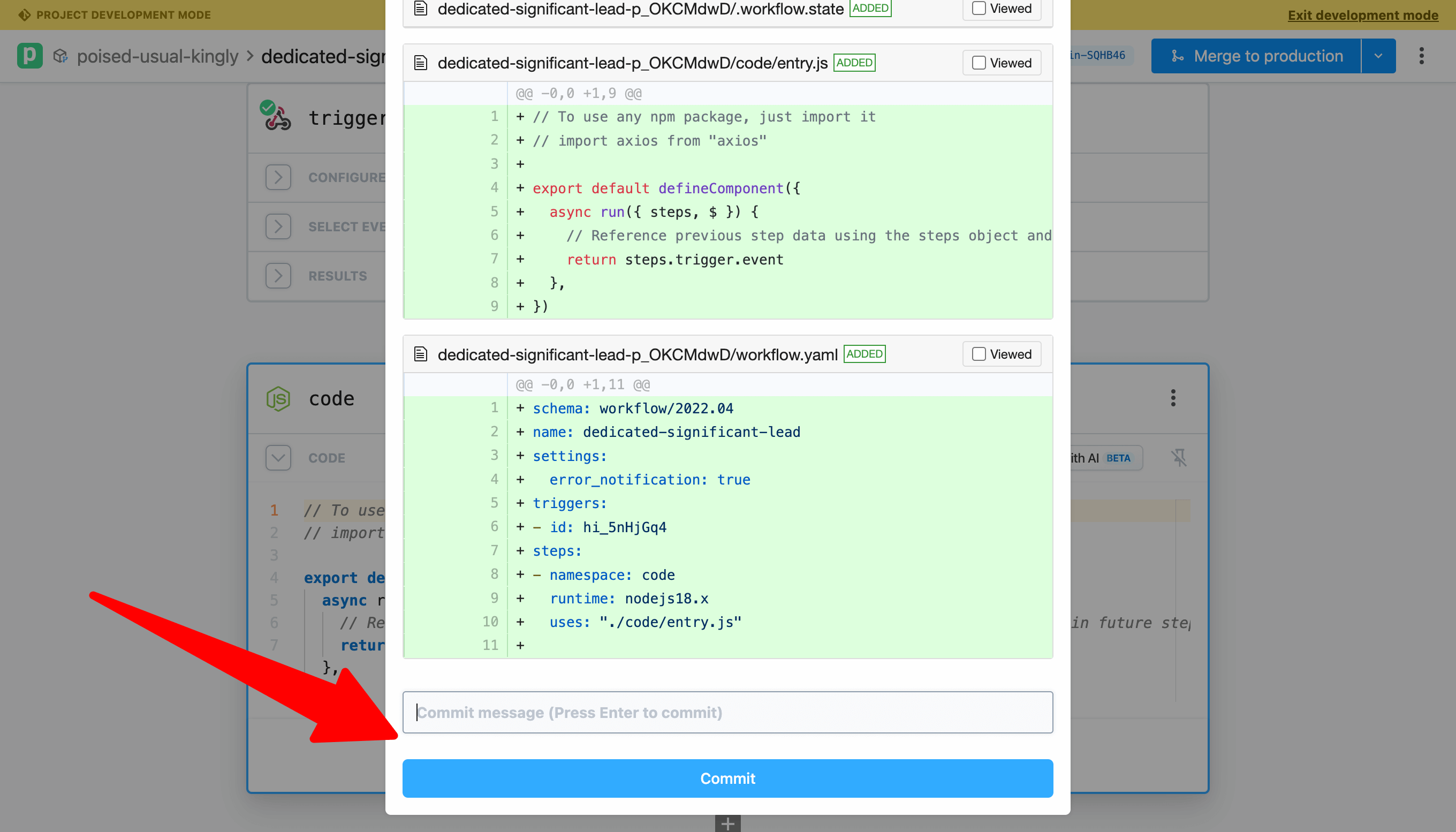
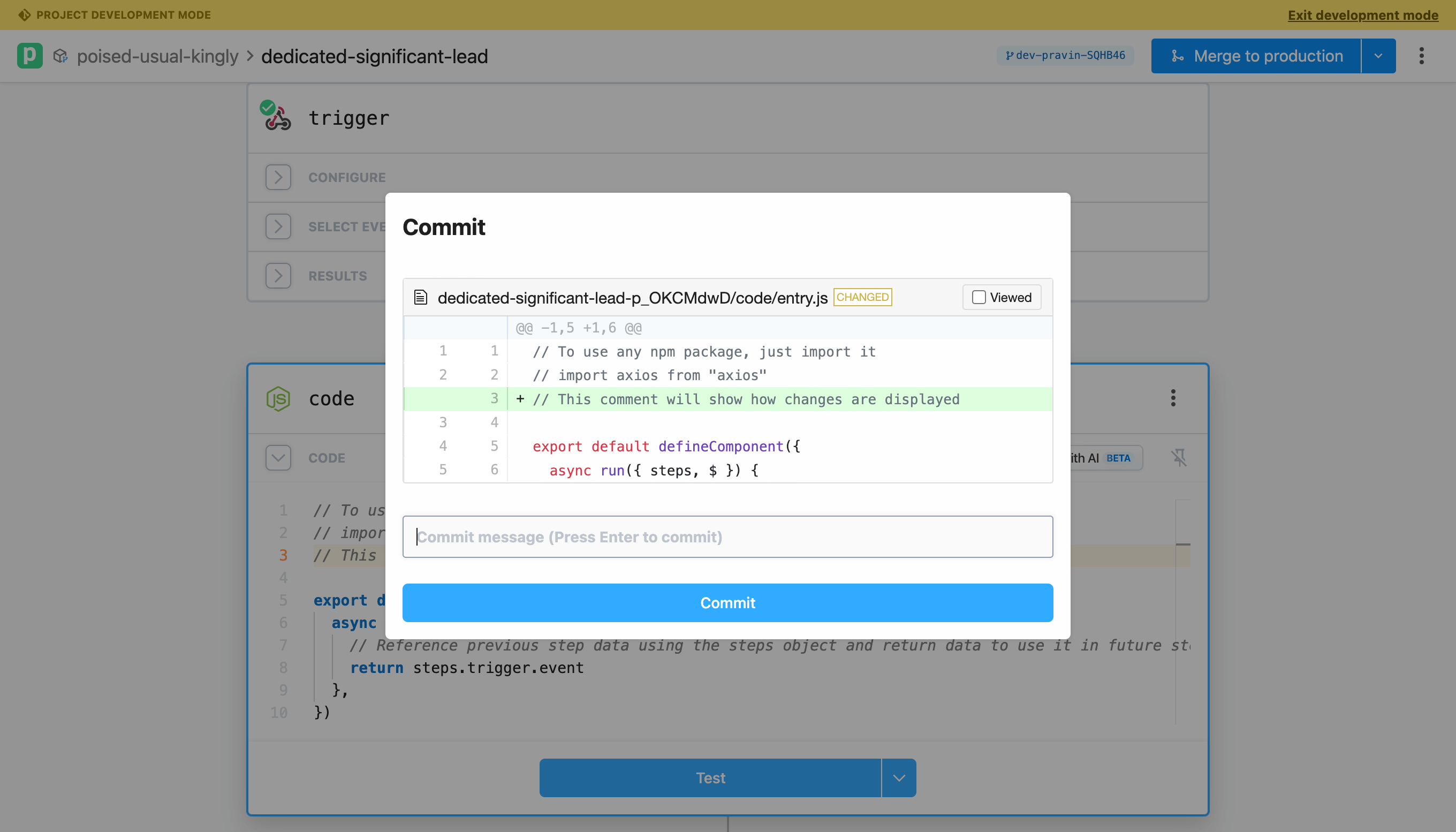
Next, make an edit to the code (e.g., add a comment). Commit your changes again. Notice that the commit diff highlights the specific changes that will be committed.
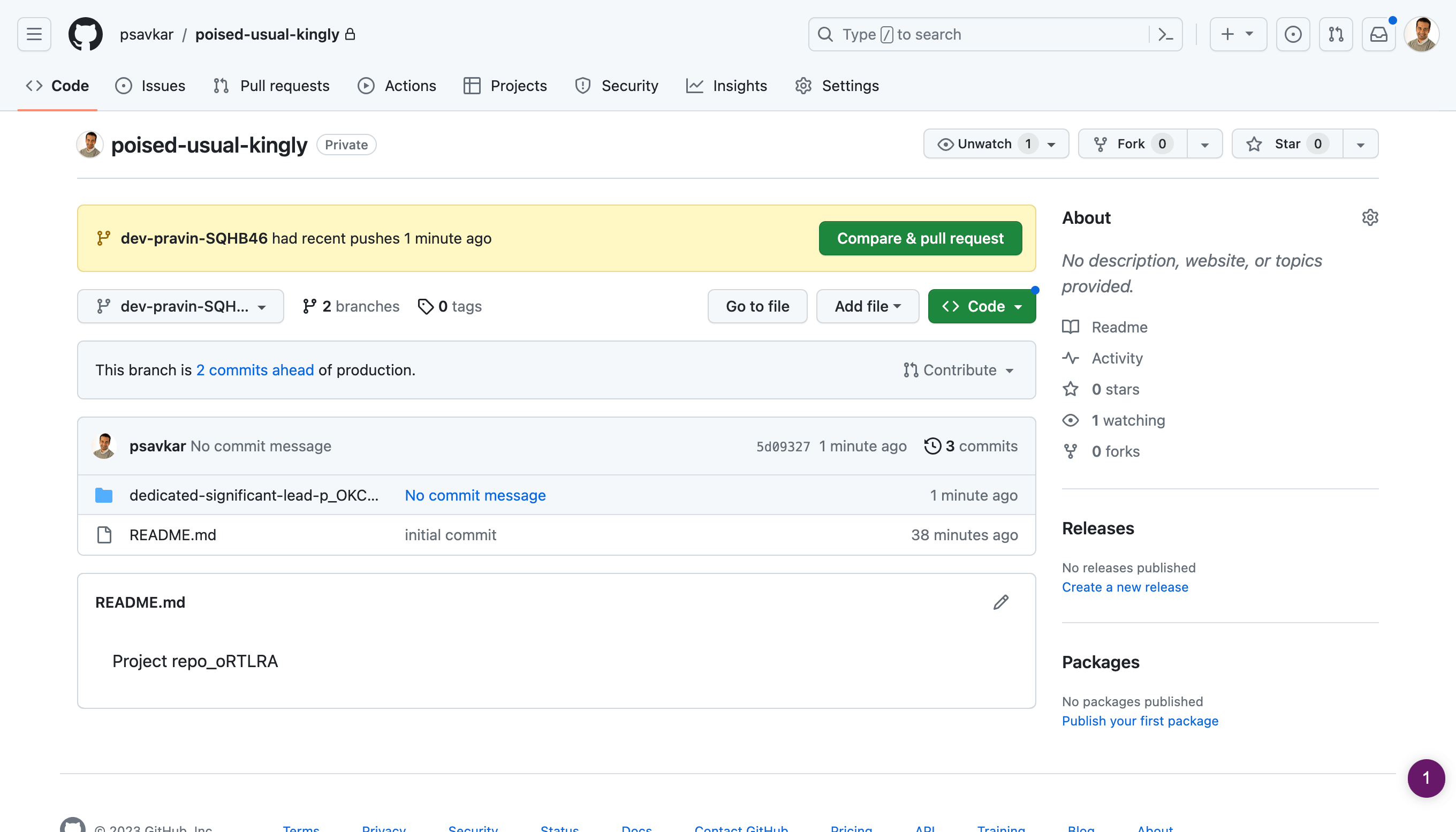
# View your project on GitHub
Open the git actions menu and select View branch on GitHub.
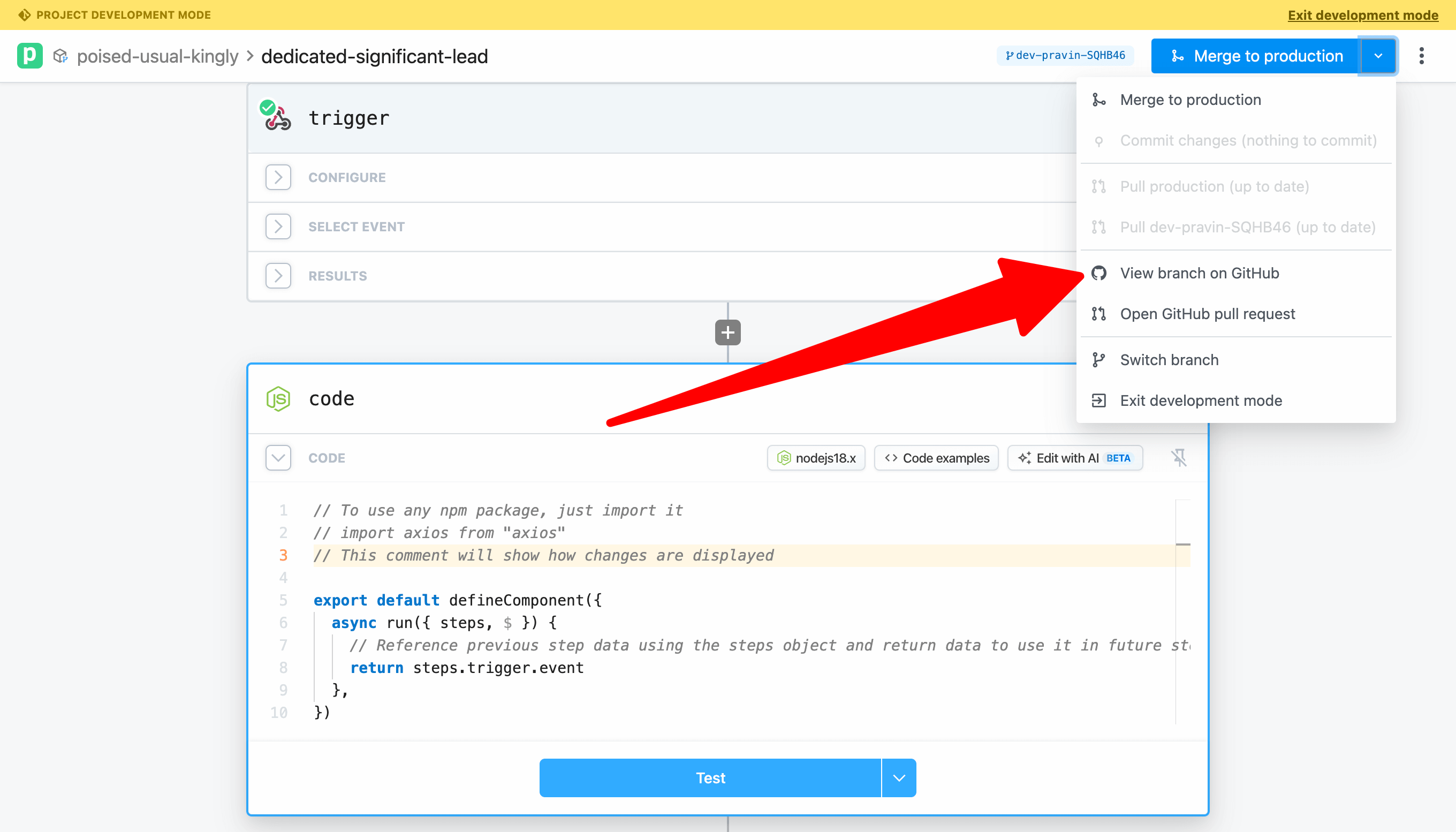
You can explore the files created, including the YAML file with the workflow definition and the javascript file with the code for the Node step.
TIP
Optionally navigate to the file with the code step and make an edit to the file and commit your changes to the branch (e.g., add another comment). When you return to Pipedream, you'll notice the git actions button will prompt you to pull changes. Pipedream's integration with GitHub is bi-directional, so you can make edits outside of Pipedream (including locally) and sync them via GitHub. Note: there are currently restrictions on local development (e.g., you can only edit existing resources -- you can't create new workflows locally).
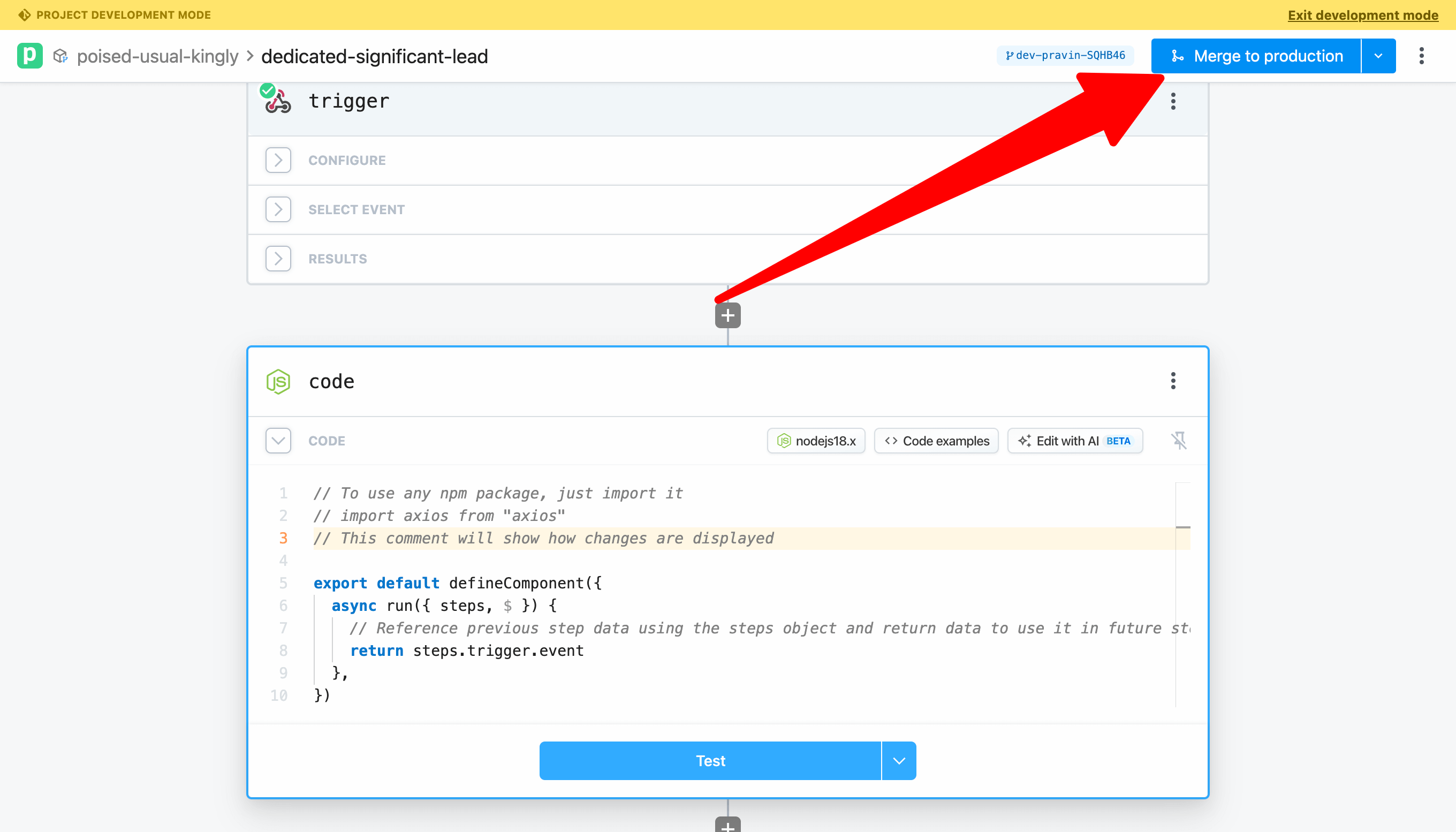
# Merge your changes to production
Merge to production to deploy the workflow to Pipedream.
Pipedream will show you the full diff of all commited changes and the current state of Production. When your changes are merged, Pipedream will route you to the production branch for the project where you can view and inspect live, running workflows and events.
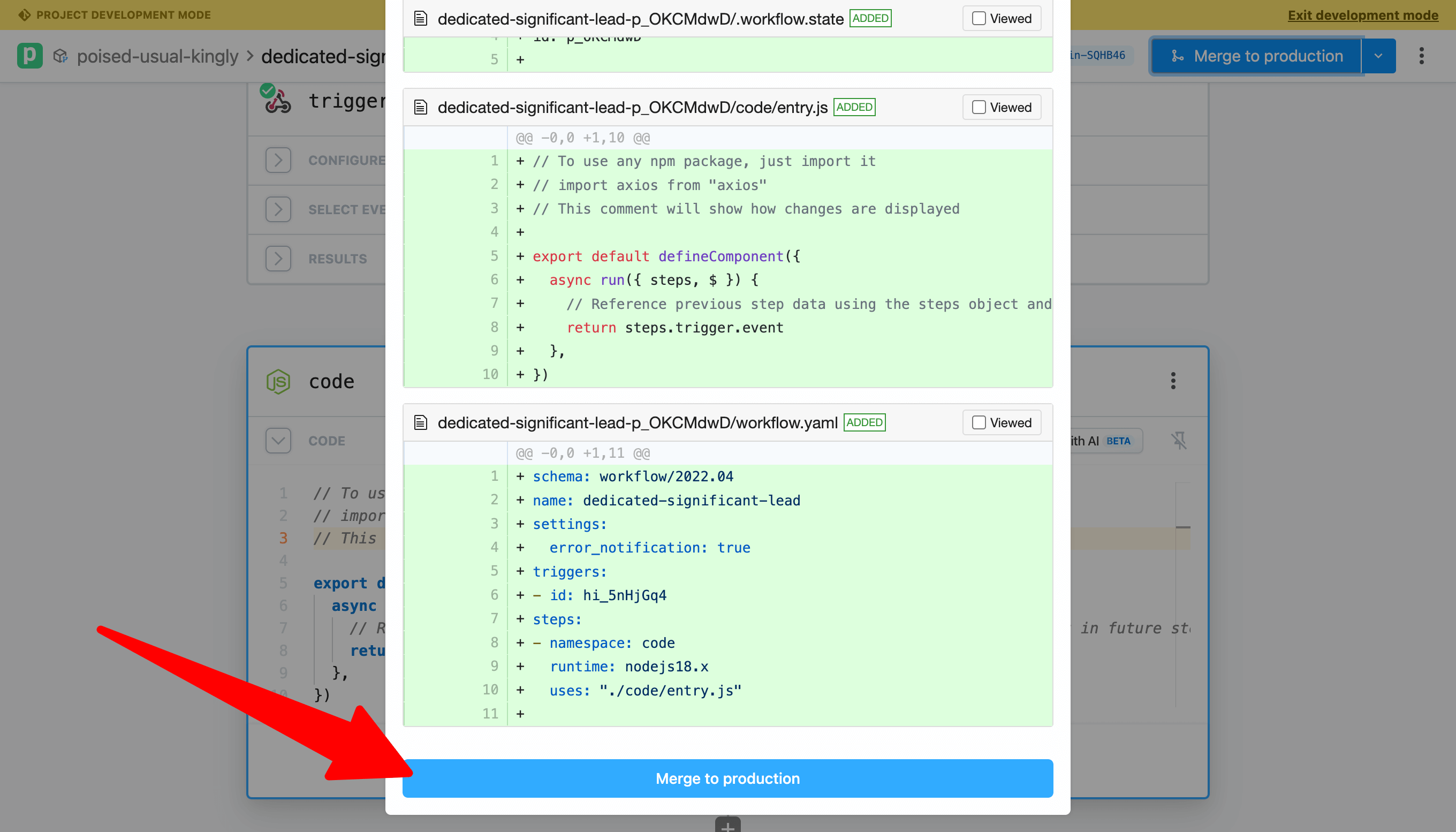
NOTE: When you merge, changes for all resources in the project will be merged. That means one or more workflows may be updated, enabled, disabled, etc.
# Edit a previously merged branch
To edit a previously merged branch, you may create a new branch or click Edit when viewing the productionto continue editing the last used branch.
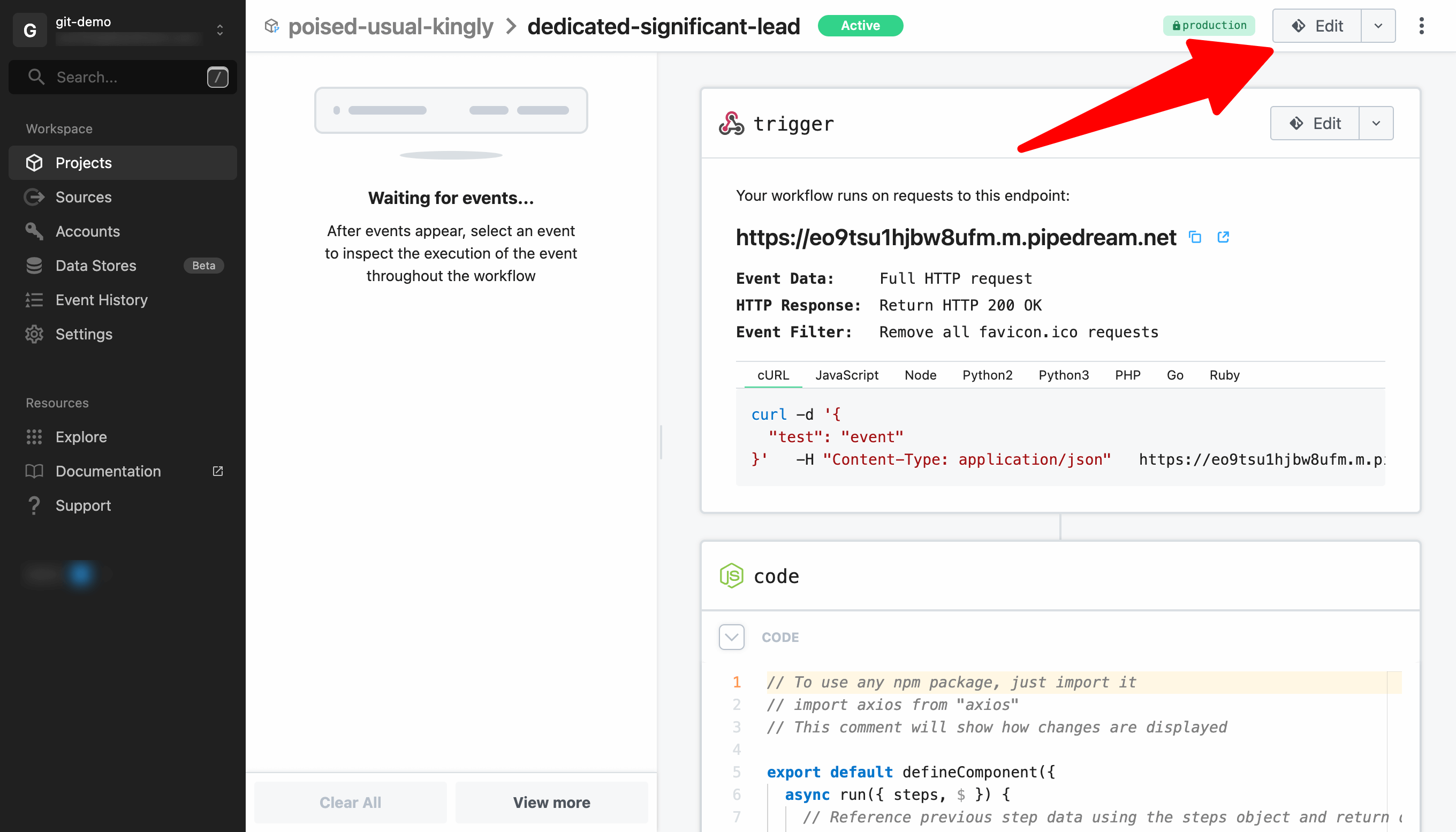
Open the workflow in Pipedream's editor and add an HTTP request action to the end of the workflow. Configure the action to GET the URL https://example.com.
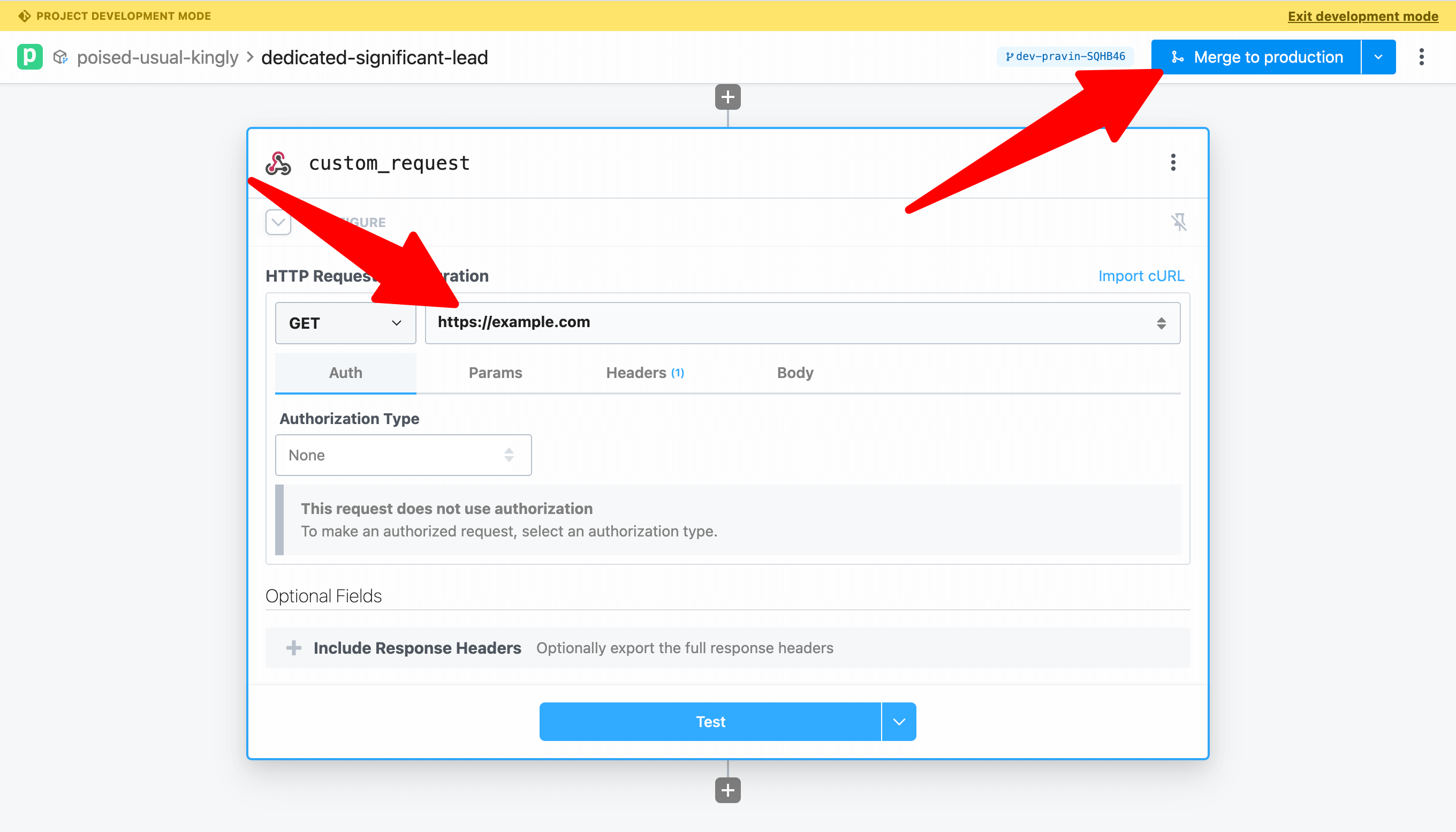
This time, we'll merge directly to production without commiting separately. Click Merge to Production to view the diff, commit and merge.
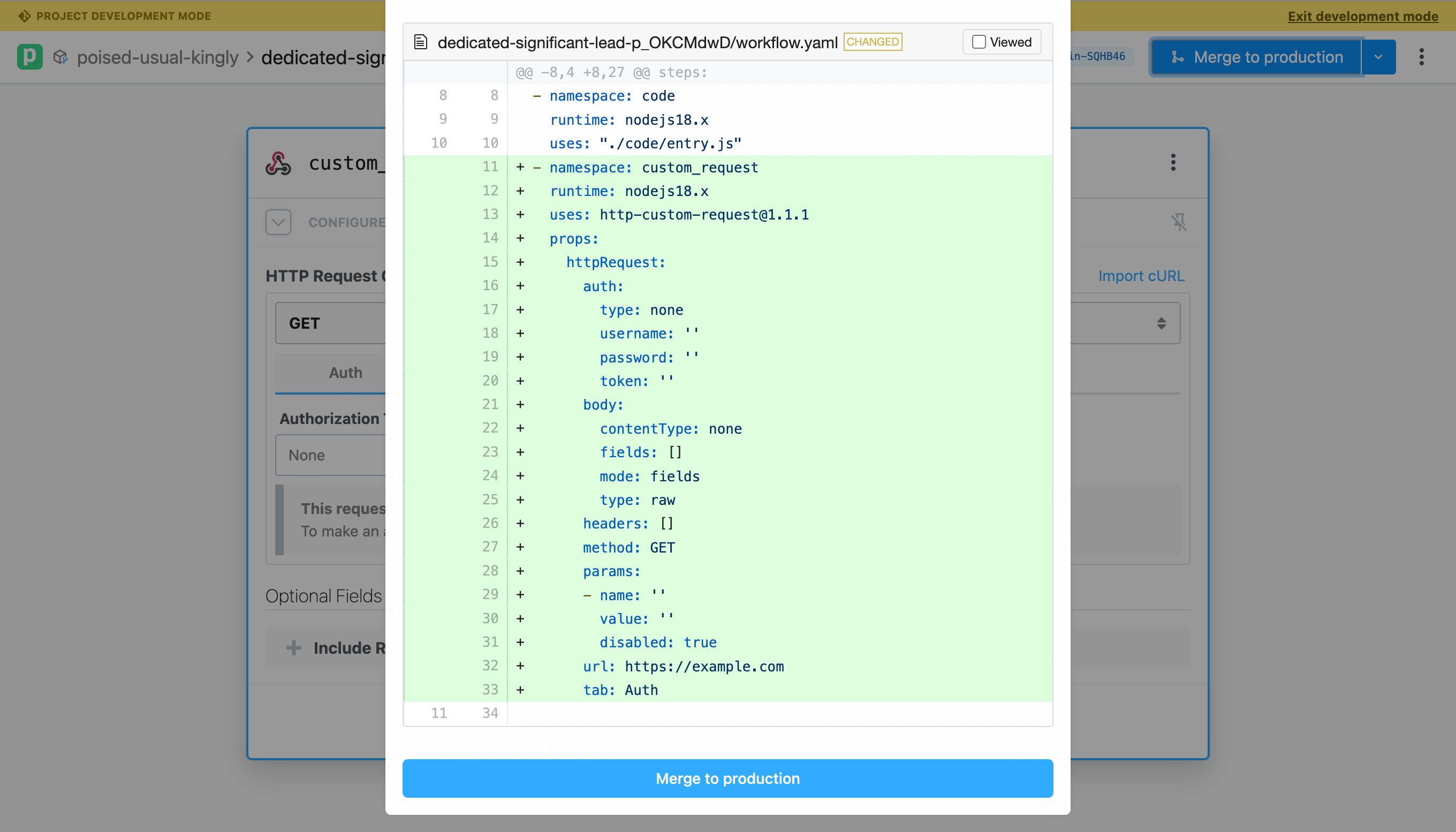
You may also view the repo on GitHub to see how the action configuration is represented in the YAML of the workflow definition. Try other actions, including actions that use connected accounts and explore how they're represented in the GitHub code.
# Make an edit and merge from GitHub
As the final step of this quickstart, view the repository on GitHub and navigate to the code step. Click the edit icon and made a simple change (e.g., add a comment).
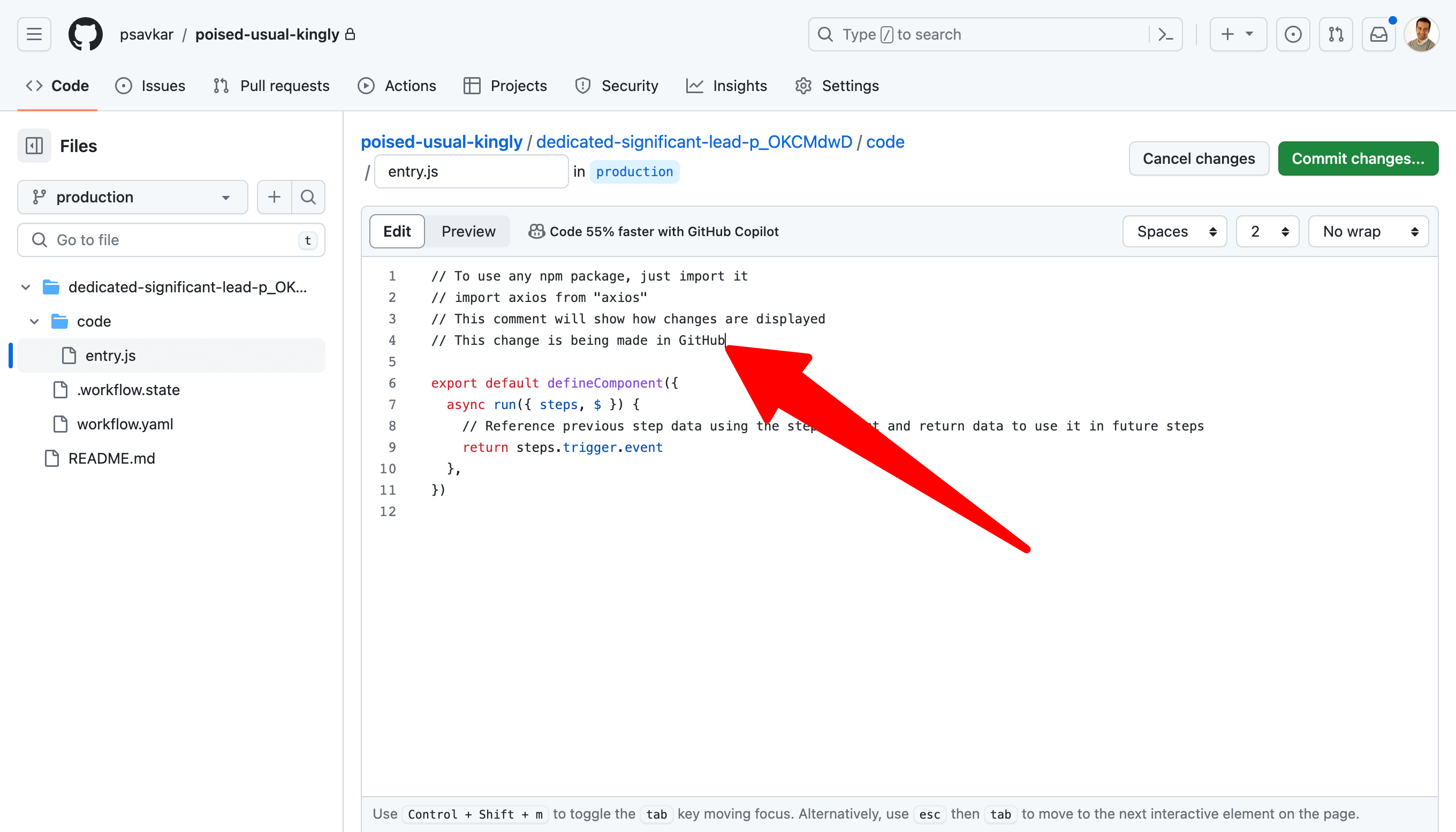
Commit and create a PR.
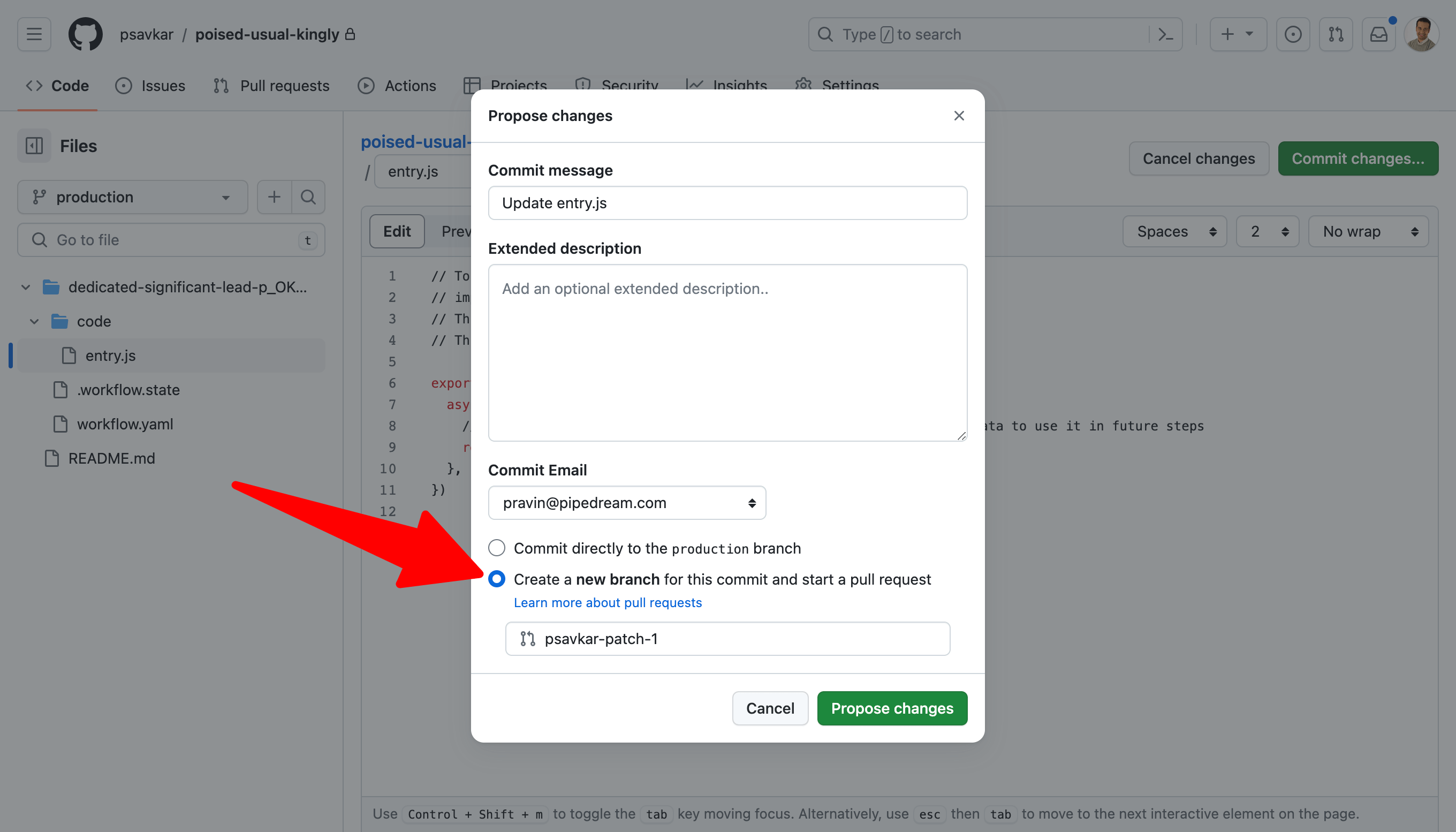
Then open the PR, review the changes and merge.
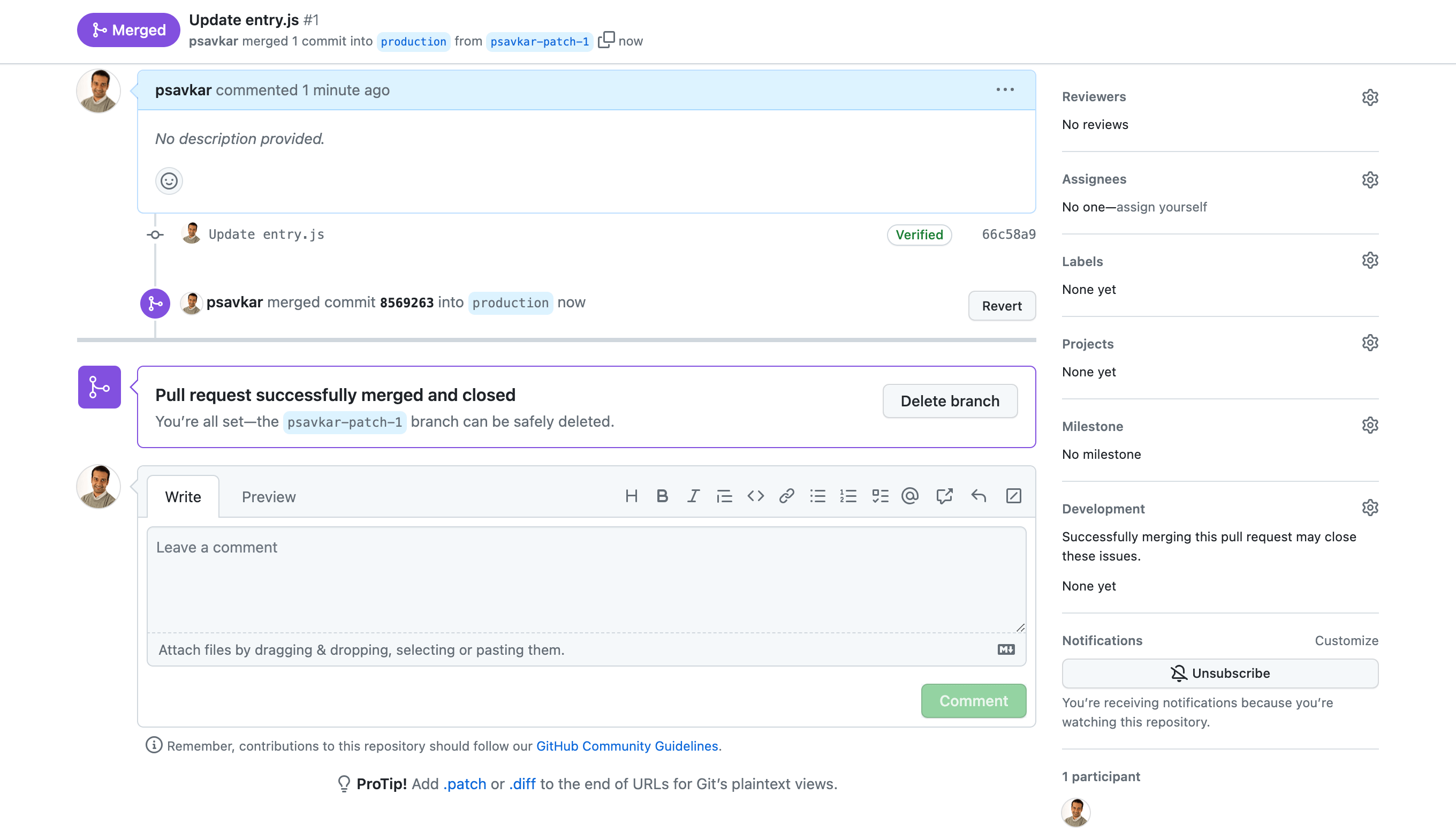
When you return to Pipedream, the changes will be merged to production and deployed.
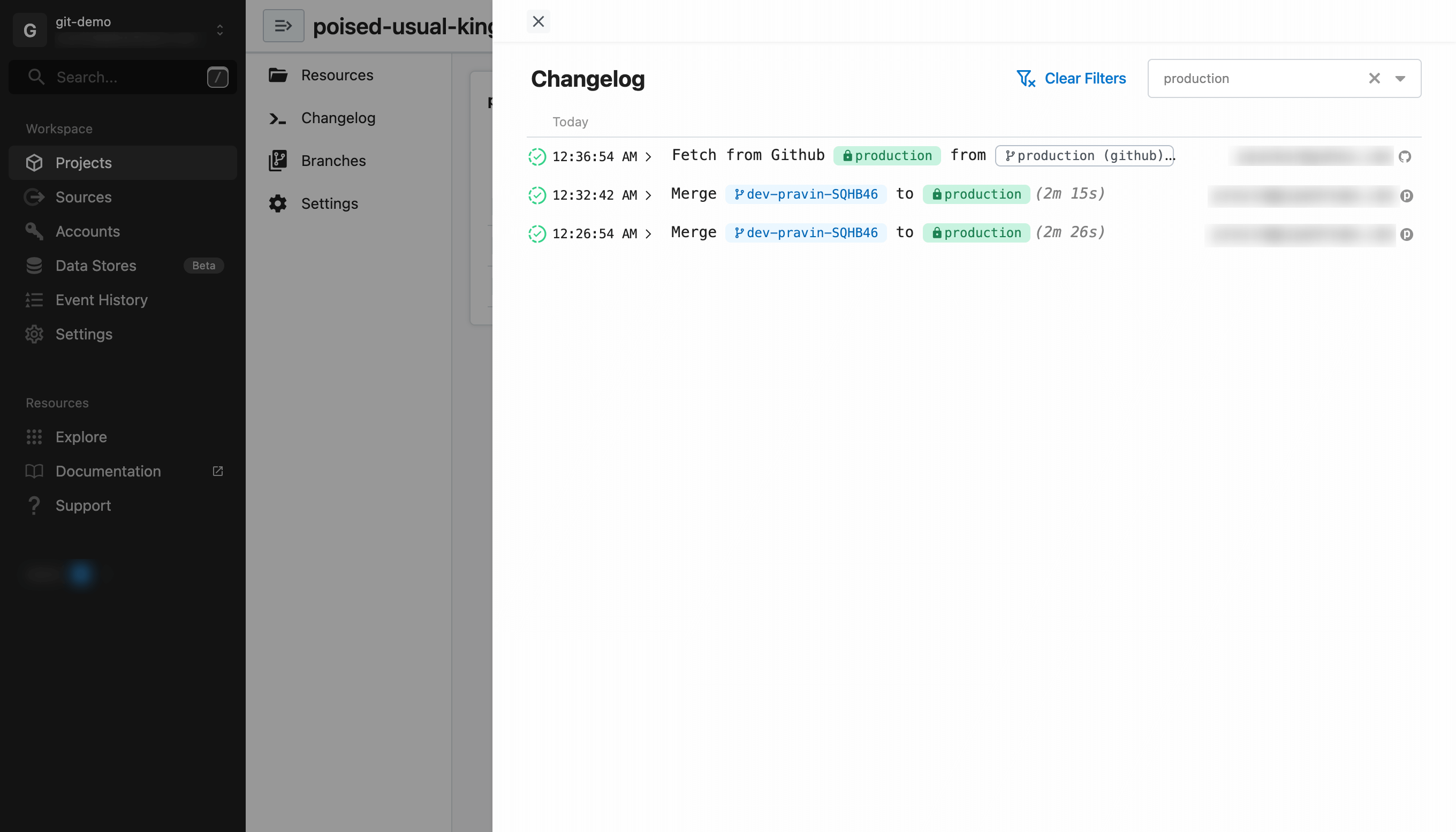
# Use the changelog
If you have any issues, including errors when merging or deploying, check the changelog. It communicates the state of all operations from both Pipedream and GitHub and will surface errors and issues (including where actions were initiated from and by whom).
# More resources
We hope that helps you get started with GitHub. Next, we suggest reading the docs and exploring the feature in more depth. If you have any issues or feedback, please reach out to Support, on public Slack or on Discourse.
